
How Much Vitamin D Do You Get from the Sun?
Updated Dec 20, 2023. Medically reviewed by Jordan Stachel, M.S., RDN, CPT. To give you technically accurate, evidence-based information, content published on the Everlywell blog is reviewed by credentialed professionals with expertise in medical and bioscience fields.
Table of contents
- Factors Impacting How Much Vitamin D You Get from Sunlight
- Guidelines for Getting Vitamin D from Sunlight Safely
- Other Sources of Vitamin D
- Monitor Your Vitamin D Intake with Everlywell
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that aids in calcium absorption and promotes immune system and bone health. [1] It occurs naturally in some (though not many) foods, and your body produces it when your skin is exposed to the sun. [1]
But there’s a caveat to this metabolic process. Your body synthesizes vitamin D from another form of the vitamin, calciferol, which is found in your skin. Its ability to meet your daily needs—600–800 IU for adults—depends on several factors, including where you live and the chemical composition of your skin. [1]
Though sunlight has long been considered one of the best sources of vitamin D3, an estimated 35% of American adults are vitamin D deficient. [2] Below, we’ll shed light on why it’s important to vary where you derive vitamin D—whether from sunlight, food, or supplements—and address the best ways to help you get your daily quota.
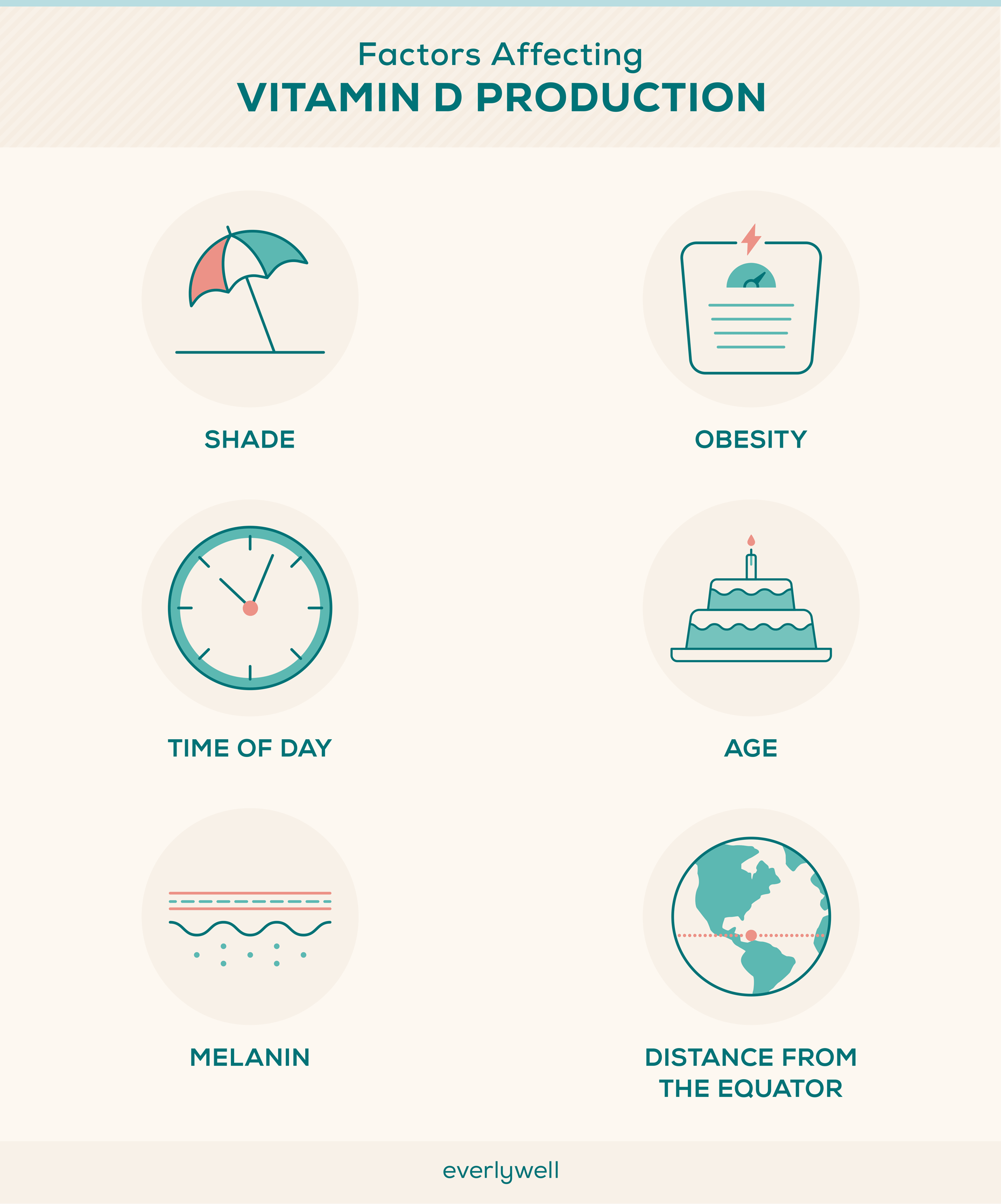
Factors Impacting How Much Vitamin D You Get from Sunlight
Experts only have a general idea of how much sunlight exposure is necessary for adults to meet their daily quota of vitamin D. Currently, it’s recommended you get 15 minutes per day (maximum) of sunlight exposure between the hours of 10am and 3pm. [3]
The amount of vitamin D your body generates from sunlight depends on several internal and external factors:
- Geography – The farther you travel from the equator, the less UVB light reaches the earth’s surface. This means that people living further from the equator have to spend more time in the sun in order to produce adequate vitamin D from sunlight. [4]
- Time of year – At certain times of year, particularly in locations exposed to less sun, vitamin D deficiency can become especially pronounced. This means you may simply be unable to produce enough vitamin D during winter. [4]
- Time of day – The sun’s rays vary in intensity throughout the day. In most places, UV rays are strongest between about 10am and 4pm, when the sun is at its peak. [5] If you go outside during that interval, your body will make more vitamin D in less time than if you went out in the early morning or late afternoon.
- Your skin’s melanin content – Melanin is a substance in the skin that absorbs UVB light to prevent sun damage. [4] The more melanin you have, the more UVB light is absorbed instead of converted into vitamin D. This means that people with darker skin generally need to spend more time in the sun than people with lighter skin to get the same amount of vitamin D. [4]
- Your age – It’s thought your body has a harder time making vitamin D efficiently as you get older. [4] Older and elderly adults also tend to spend less time outdoors. As a result, people ages 70 and older may be at a higher risk of developing a vitamin D deficiency. [6] This is why healthcare providers often recommend vitamin D supplementations to older adult patients.
- Your body composition – Vitamin D is fat-soluble, meaning that it’s stored by fat cells after being ingested through food or produced by your body. [7] Because fat cells store and retain vitamin D, people with excess body fat are more likely to be vitamin D deficient. [8]
Importantly, your body is capable of producing vitamin D even if it isn’t in direct sunlight. [9] When you sit in the shade, your skin is exposed to scattered UVB rays. Though these aren’t as strong as direct sunlight radiation, they still trigger the body to produce some vitamin D with exposure—while minimizing your chances of significant sun damage.
Sitting in the shade is a recommended option if you [5]:
- Need to spend extended periods outside, like working in an outdoor profession
- Have a skin type or condition that makes you more vulnerable to sun damage
- Are very careful about minimizing your risk of skin cancer

Guidelines for Getting Vitamin D from Sunlight Safely
While sunlight is important for vitamin D production, UVB rays will cause skin damage over time. Overexposure to sunlight can cause sunburns and increase the risk of developing skin cancer, so it’s important to take the following precautions when spending time in the sun. [5]
Limit Your Time in the Sun
The chance of sun damage increases the longer you stay outside. Risks are especially potent if:
- You have less melanin in your complexion
- You are highly sensitive to sunlight
- You have a condition like albinism, which causes your body to produce little or no protective melanin [10]
- You’re spending time outdoors at a higher altitude, or near surrounding water, ice, or snow [5]
To reduce the risk of harm, try limiting the time you spend in the sun. Alternatively, you can break up your sun exposure into short intervals. If you aren’t sure how much time could put you at risk of sun damage, you can also ask your healthcare provider for advice.
Use Sunscreen
It’s important to apply sunscreen any time you plan on spending more than 15 minutes in direct sunlight. To ensure you’re protected:
- Apply sunscreen to exposed areas at least 30 minutes before venturing outside.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or directly after intense physical activity or activities that expose you to water (like swimming).
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends using a water-resistant, broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect you from both UVB and UVA rays. [11]
Remember that while sun protection reduces the amount of UV rays penetrating the skin, it will not inhibit your body from producing vitamin D. Even if you do cover all exposed skin with sunscreen, it’s estimated that between 2 and 7% of UVB rays will still reach your skin. [12]
Protect Your Face and Eyes
When spending time outdoors, many people leave their faces and eyes exposed without effective sun protection, making them vulnerable to sun damage and photoaging. [13] Over time, sun exposure can damage the eyes and lead to [12]:
- Cataracts
- Eye cancers
- Eye growths
To protect your face and eyes from the sun, try wearing hats or UV-blocking sunglasses. If you’re worried about facial blemishes, you can try a facial sunscreen designed to protect against sun damage without causing comedones, clogging pores, or irritating sensitive skin.
Other Sources of Vitamin D
Many people don’t get enough vitamin D from the sun alone, especially if they spend most of their time indoors or live far from the equator. Too much sun exposure can also lead to skin damage and cancer, so many healthcare providers recommend relying on other sources of vitamin D. [14]
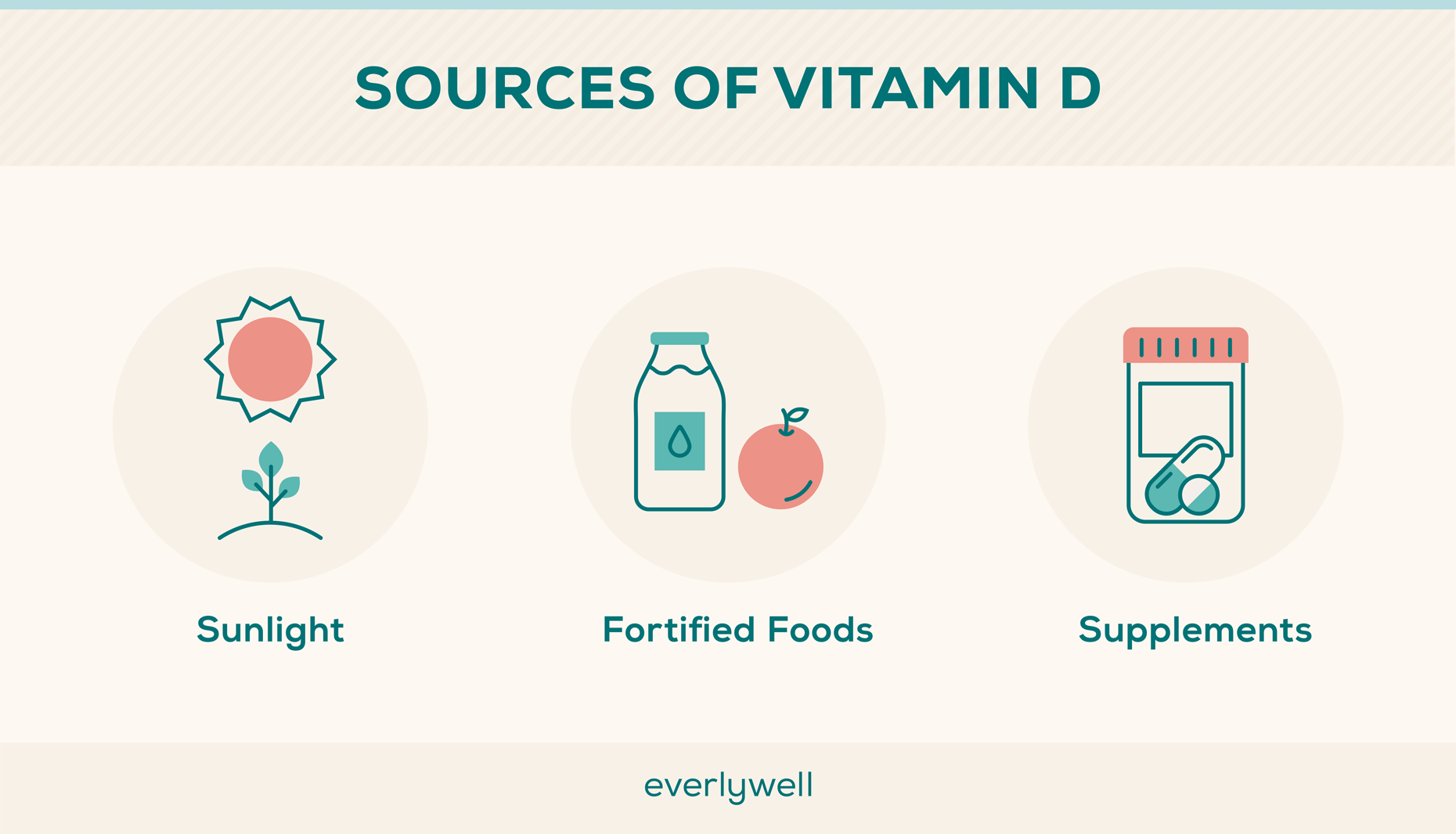
Vitamin D-Fortified Foods
Adding healthy foods rich in vitamin D to one’s diet can be an effective way to help prevent deficiency. Vitamin D3 occurs naturally in some foods, while others are fortified with vitamin D2 during manufacturing.
If you live in a place that gets little sunlight or have a sensitive skin type, consider adding the following foods to your diet:
- Egg yolks
- Mushrooms
- Herring
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Fortified milk
- Fortified yogurt
- Fortified orange juice
- Fortified tofu
Supplements
Vitamin D supplements can be an effective option for people who can’t get enough vitamin D through their diet. You can find over-the-counter vitamin D supplements at most pharmacies and grocery stores.
Before buying a vitamin D supplement (or any dietary supplement) it’s important to examine your supplement labels. Supplements that contain more than the daily recommended quota of vitamin D could lead to problems like stalled digestion or kidney damage with habitual use. [1]
Moreover, supplements aren’t regulated by the FDA, so be sure to choose one produced by a trusted vendor. Before introducing any new supplement to your regimen, it’s also best to consult with a health professional to ensure that you aren’t taking too much for your body and health history.
Monitor Your Vitamin D Intake with Everlywell
If you take steps to protect your skin and don’t overdo it, spending time in the sun can be a supportive way to get some extra vitamin D. However, if you’re vitamin D deficient or need a surefire source to meet your needs, consider introducing vitamin D supplements to your wellness routine.
With Everlywell, you can get vitamin D supplements you can trust and test for deficiencies at home with the Everlywell Vitamin D Test. Find out more by browsing the Everlywell Nutritional Health test range today.
References
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2023, August 10). Vitamin D. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- professional, C. C. medical. (n.d.). Vitamin D deficiency: Causes, symptoms & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2018, October 31). Mayo Clinic Q and a: Getting enough vitamin D - Mayo Clinic News Network. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- 6 things you should know about vitamin D. Harvard Health. (2020, October 13). URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation and Sun Exposure | US EPA. (n.d.). URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Wei, J., Zhu, A., & Ji, J. S. (2019, December 23). A comparison study of vitamin D deficiency among older adults in China and the United States. Nature News. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Vitamin D, obesity and covid-19. UC Health. (n.d.). URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- professional, C. C. medical. (n.d.-a). Vitamin D deficiency: Causes, symptoms & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Vitamin D. The Nutrition Source. (2023, March 7). URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2023b, December 13). Albinism. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Foundation, S. C. (2023, May 23). Ask the expert: Does a high SPF protect my skin better?. The Skin Cancer Foundation. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Foundation, S. C. (2023b, October 24). Sun Protection and vitamin D. The Skin Cancer Foundation. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Yale Medicine. (2023, October 19). Photoaging (sun damage). Yale Medicine. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
- Moriarty, C. (2018, March 15). Vitamin D myths ’d’-bunked. Yale Medicine. URL. Accessed December 19, 2023.
Jordan Stachel, M.S., RDN, CPT is most fulfilled when guiding others towards making stepwise, sustainable changes that add up to big results over time. Jordan works with a wide variety of individuals, ranging in age from children to the elderly, with an assortment of concerns and clinical conditions, and has written for publications such as Innerbody. She helps individuals optimize overall health and/or manage disease states using personalized medical nutrition therapy techniques.