
Thyroid Disease and Sleep Loss: What You Need to Know
Sleep is vital to everyone’s health, and experiencing sleep loss at night or fatigue during the day can impact many aspects of your life. This is especially true if you have a thyroid disease like hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Thyroid hormones help regulate your metabolism, determine your heart rate, and are involved in the proper functioning of almost every organ system in the body. If your thyroid isn’t working correctly and you’re lacking sufficient hormone levels, it can cause a number of health problems, such as fatigue or sleep loss.
If you’ve experienced drops in your energy levels due to a thyroid condition, read on or skip to our infographic to understand the link between thyroid disease and sleep loss.
How Does Thyroid Disease Impact Sleep?

Too much thyroid hormone production suggests an overactive thyroid, also known as hyperthyroidism. Since this disorder over-stimulates the nervous system, it can lead to rapid heart rate, night sweats, and anxiety—all of which can disrupt your ability to relax or get a good night’s sleep, leaving you fatigued.
Having too little thyroid hormone production can indicate an underactive thyroid, otherwise known as hypothyroidism. This may cause you to feel fatigued, lack energy, experience weight gain, experience forgetfulness, or even depression.
6 Ways to Improve Your Sleep with Thyroid Disease
If having a thyroid disease is behind your sleep loss, consider adding a few of our tips to your bedtime routine.
Manage nighttime stress or anxiety with deep breathing

When it comes to thyroid conditions, symptoms like rapid heart rate, anxiety, and nervousness can feel uncomfortable and can cause a person to feel stressed, affecting their ability to relax and get a good night’s sleep. Practicing deep breathing before bed can be a very effective relaxation technique to help alleviate insomnia caused by stress or anxiety symptoms. It can even slow your heart rate by allowing you to keep your breath, body, and mind steadied and controlled.
To properly do this, the National Sleep Foundation recommends that, before bed, you turn all your attention to your breathing pattern. Then visualize your airflow as it passes through your mouth and airways, down to your belly, and back out again. Counting your breath as you inhale and exhale can help promote slow and steady breathing.
Lower your body temperature by taking a warm bath before bed

Taking a warm bath or shower before bed can help you unwind and improve your sleep. The “warm bath effect,” as some researchers refer to it, suggests that by taking a dip in warm water not immediately before but prior to bed may improve your quality of sleep.
Staying in a hot shower or bath for as little as 10 minutes can help improve your ability to relax your body, fall asleep, and stay asleep. It’s recommended to schedule this one to two hours before your bedtime to allow your body temperature to lower and for tiredness to set in.
Reduce night sweats by keeping your bedroom cool

If you have hyperthyroidism, you may find yourself feeling hot when you sleep or suffering from night sweats. Keeping your room cool will not only help your body relax and fall asleep, but can also help prevent you from waking up covered in sweat.
Lowering the temperature in your bedroom, hanging blackout curtains, or switching to cooling bedding are all ways to help keep the temperature of the room—and your body—from rising uncomfortably.
Before doing this, make sure you’re comfortable in cooler temperatures as those with a thyroid condition may also experience sensitivity to cooler climates or temperatures.
Alleviate stress by exercising

Taking time during the day to exercise can promote a good night’s sleep. Your body’s ability to get better sleep after exercise can be attributed to a number of factors. Exercise increases your body’s production of endorphins—which can help manage feelings of stress and anxiety. This may make it easier to relax your mind and unwind at night so your body can drift into a calm sleep.
Help manage thyroid symptoms by eliminating stress

Feeling stressed could make the symptoms of your thyroid condition worse—so do what you can to eliminate stress throughout the day and before bed. If you’re unsure if stress is contributing to your sleepless nights, it may be helpful to take a sleep and stress test to see if key hormones involved in your sleep-wake cycle may be contributing to stress and sleep loss.
Boost energy levels by maintaining a healthy diet

Improving your diet may improve your metabolism, which could give you more energy throughout the day, potentially improving daytime fatigue. Eating regularly and filling your plate with multiple food groups (whole grains, lean protein, fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, and low-fat dairy) are ways to optimize your diet to boost your energy levels. Eating healthy snacks with lean protein and fiber-rich carbohydrates can also provide you with lasting energy during the day and reduce feelings of fatigue.
Common Symptoms of a Thyroid Condition
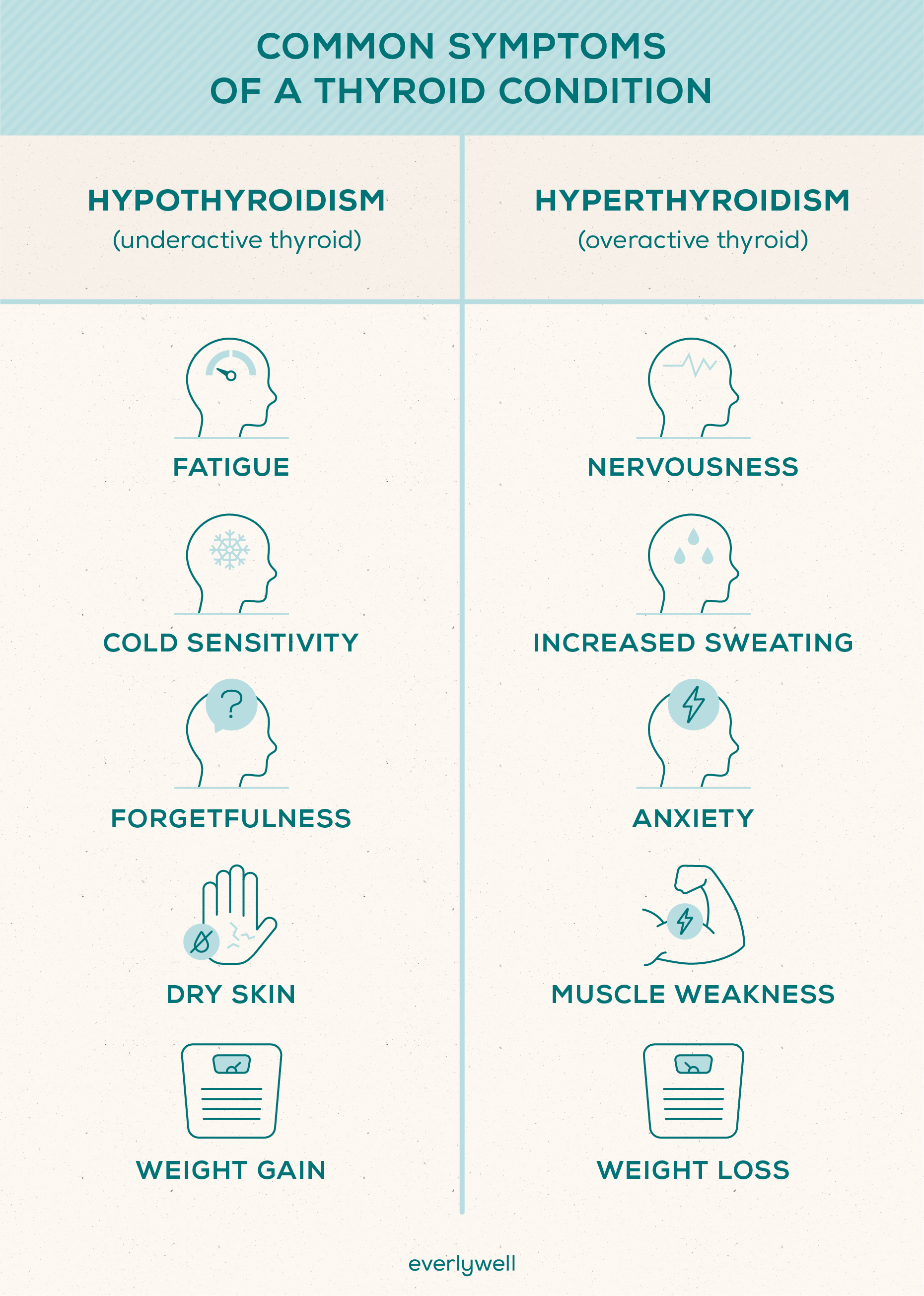
Experiencing new or unusual symptoms may be your first indication of a thyroid condition. Depending on the type of thyroid condition, symptoms will differ. However, common signs to look out for include: lack of energy, unintended weight changes, muscle weakness, hair loss, increased sweating, or temperature sensitivity (frequently feeling too hot or too cold).
While women are more likely to develop a thyroid condition, especially after pregnancy or menopause, anyone who is experiencing symptoms of thyroid disease should consider speaking with their healthcare provider and testing their thyroid hormone levels. For ease and convenience, consider an at-home thyroid testing option so you can fit it into your schedule at any time.
If your healthcare provider has diagnosed you with insufficient or excess thyroid hormones, there are several treatment options to help you manage the condition and improve your quality of life. Depending on the type of thyroid condition you have, treatment may differ.
For instance, those with hypothyroidism are often treated with medicine that gives the body a sufficient amount of thyroid hormone for the thyroid gland to work normally. These medications may need to be taken for the rest of your life or as long as your doctor prescribes, and may require follow-up testing to evaluate the effectiveness of the medication or dose.
Treatment for hyperthyroidism is commonly aimed at reducing the overproduction of thyroid hormones through antithyroid medication, thyroid surgery, or other options.
If sleep loss continues to be a problem, speak to your healthcare provider—they may have recommendations to help you further manage your thyroid symptoms, or any other condition that may impact your sleep. If you’re experiencing symptoms and are concerned you may have a thyroid disorder, an at-home thyroid panel is an option, though know that ultimately only a healthcare provider can diagnose you with a thyroid condition. Finally, don’t forget to keep an open dialogue with your healthcare provider about your test results, concerns, and symptoms as most thyroid conditions can be treated with their help.

Sources: National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine | Office on Women's Health | Mayo Clinic | Mayo Clinic | National Sleep Foundation | Frontiers in Neuroscience | Penn Medicine | National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine | Endocrine Web | Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics