
What Are the Warning Signs of Prediabetes? Risk Factors, Diagnosis, and Reversal
Medically reviewed by Neka Miller, PhD on May 15, 2020. To give you technically accurate, evidence-based information, content published on the Everlywell blog is reviewed by credentialed professionals with expertise in medical and bioscience fields.
Along with a healthcare provider’s evaluation, an HbA1c test may help you find out if you have prediabetes. You can easily check your A1c levels from the comfort of home with our at-home [HbA1c](https://www.everlywell.com/products/hba1c/) test.
Table of Contents
- What Is Prediabetes?
- Common Symptoms and Warning Signs of Prediabetes
- Risk Factors
- Tips To Reverse Prediabetes
- How Do I Know if I’m Prediabetic?
About 96 million (1 in 3) adults in the United States have prediabetes. While prediabetes is extremely common, it is a serious health condition that can develop into type 2 diabetes if left untreated. If you think you could have this condition, you might be wondering: What are the warning signs of prediabetes, and is it reversible?
Fortunately, knowing the warning signs can lead to an early diagnosis and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes down the road. Continue reading to learn more about prediabetes, the warning signs, and lifestyle changes that can help reverse it.
What Is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes occurs when blood sugar levels are higher than normal but do not require a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. As a result, people with prediabetes are more likely to develop diabetes if their blood sugar gets too high. High glucose levels associated with prediabetes can also start damaging your blood vessels, heart, and kidneys.

A healthcare provider may diagnose you with prediabetes if you have:
- A hemoglobin A1c test result between 5.7% and 6.4%
- A fasting blood glucose test result between 100 and 125 mg/dL
- An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) between 140 and 199 mg/dL two hours after starting the test
In a person who doesn’t have prediabetes, sugar from food enters the bloodstream during the digestion process. The pancreas then makes insulin, which circulates through the blood and allows sugar to enter the cells, lowering blood sugar levels.
If you have prediabetes, the process doesn’t work the same way. Instead, the pancreas either doesn’t make enough insulin, or the cells become resistant to it (insulin resistance). As a result, the sugar in your body doesn’t provide enough fuel for the cells and builds up in the bloodstream, causing high blood sugar.
Receiving a prediabetes diagnosis doesn’t mean that developing diabetes is inevitable. It just means that you have to watch out for the warning signs and take steps to keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs of Prediabetes
Prediabetes doesn’t always produce any immediate signs or symptoms, making it difficult to detect. That’s why an estimated 8 out of 10 people with prediabetes don’t even know they have it. However, people with prediabetes may experience one or more of the following symptoms:

Frequent Urination and Increased Thirst
Excess glucose in the blood can lead to frequent urination in people with prediabetes. As blood glucose levels increase, the kidneys have to work harder to filter it out. Extra glucose is then excreted into the urine, which pulls extra fluids from other tissues in the body and causes dehydration. People with prediabetes often drink more fluids to combat dehydration and have to urinate more often as a result.
Increased Hunger
After you eat, carbohydrates from food are broken down into glucose, the body’s main energy source. Insulin then helps glucose enter the body’s cells to provide energy. However, people with prediabetes may not have enough insulin to absorb glucose properly. This can lead to increased hunger as their bodies attempt to make up for the deficit.
Slow-Healing Wounds
Wounds that take longer to heal are a common sign of prediabetes and diabetes. High blood glucose levels can impair blood flow, which impacts the natural healing process. This can lead to slower-healing wounds and more frequent infections in people with prediabetes.
Blurred Vision
Over time, high blood glucose levels can lead to blurred vision and vision loss. High blood glucose levels can cause the body to pull moisture from tissues, including the lenses of the eyes. This can make it more difficult for the eyes to focus and will make objects appear blurry.
Fatigue
Glucose is one of the body’s main sources of energy. If you have prediabetes, your body may not be able to process gluten properly and impact your energy levels. Fatigue is also a common symptom of dehydration. People who are frequently dehydrated due to high blood glucose levels might feel tired and run down—even after drinking fluids.
Tingling in the Hands and Feet
Prediabetes can increase the risk of developing diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), a type of nerve damage that often affects the feet, hands, and legs. Tingling and numbness in these areas are one of the most common symptoms of DPN. While DPN is most common in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, it’s possible for symptoms to present in people with prediabetes as well.
Acanthosis Nigricans
Acanthosis Nigricans is a condition that causes dark, velvety patches to appear on the skin in the neck, armpit, and groin areas. This condition is caused by increased insulin in the blood and can be a sign of prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Risk Factors
It’s important to be aware of the risk factors of developing prediabetes, especially if diabetes runs in your family. Here are some of the most common risk factors to look out for:
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. When a person has more fatty tissue, especially around the abdomen, cells are more likely to become insulin resistant, which increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Family history of type 2 diabetes: Having a parent, sibling, or another family member with type 2 diabetes can increase your risk of developing the condition. If you begin experiencing symptoms of prediabetes, consider asking your immediate family members about their history with type 2 diabetes to help prepare for an appointment with your healthcare provider.
- Sedentary lifestyle: the less exercise you get, the more likely you are to develop prediabetes. Regular physical activity can control weight and help the body use insulin more effectively.
- Diet: You’re more likely to develop prediabetes if you consume a lot of red meats, processed foods, or sugary beverages. To help reduce the risk, try limiting these foods and seeking out healthier alternatives to sugar.
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): Studies show that OSA can increase the risk and severity of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. If you have an OSA diagnosis, talk to your healthcare provider about your risk of developing prediabetes and what you can do to prevent it.
- Age: The risk of developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes increases as you age. If you are 45 or older, it can be helpful to discuss the risks with your healthcare provider and make any recommended lifestyle changes early on.
- Smoking Tobacco: Smoking is one more risk factor to consider. If you smoke tobacco products, you’re more likely to experience insulin resistance, putting you at an increased risk of developing prediabetes.
Tips To Reverse Prediabetes
If you have prediabetes, you might be wondering: Can prediabetes go away? Fortunately, it is possible to reverse prediabetes but it can take many years and requires a series of lifestyle changes. To reduce the risk of prediabetes developing into type 2 diabetes, consider making the following lifestyle changes:

- Exercise regularly: Because obesity increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider may recommend a healthy exercise routine to reduce excess body fat. Exercising regularly can also help stabilize glucose levels and improve circulation.
- Avoid sugary and processed foods: Consuming processed or sugary foods and drinks can worsen symptoms and increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. To help reverse prediabetes, ask your healthcare provider about healthier alternatives and try limiting sugar in your diet.
- Avoid smoking: Because tobacco products can contribute to prediabetes, limiting their use or avoiding them altogether can improve symptoms and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Eat more fiber-rich foods: A diet high in fiber can help your body control blood sugar levels and aids in digestion. Fiber helps slow digestion, which in turn slows the release of sugar into the bloodstream. Good sources of fiber include black beans, lima beans, avocados, broccoli, turnips, oats, and barley.
- Add protein to your diet: Eating plenty of protein can help slow the rate of carbohydrates entering the bloodstream, stabilizing blood sugar levels. Some healthy sources of protein include beans, broccoli, eggs, fish, lean meats, tofu, nuts and seeds, lentils, and quinoa.
- Take any prescribed medications: If your healthcare provider diagnosed you with prediabetes, they may prescribe medication to help manage insulin and blood sugar levels. Be sure to take any medication as prescribed to ensure that it has the desired effect.
- Manage stress levels: While stress alone doesn’t cause diabetes, research shows that high stress levels could interfere with insulin-producing cells in the pancreas and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If you experience high levels of stress, ask your healthcare provider about strategies to mitigate stress and anxiety.
- Get enough sleep: Getting plenty of sleep is essential for maintaining energy, supporting healthy digestion, and lowering blood sugar levels. In fact, even short-term sleep deprivation can increase the body’s insulin resistance and raise blood sugar levels over time. If possible, try to get at least 7–8 hours of sleep each night to help combat prediabetes-related insulin resistance.
- Find support: Making multiple diet and lifestyle changes is hardly easy. If you find yourself struggling with big changes, try reaching out to a trustworthy friend, family member, or support group for help.
How Do I Know if I'm Prediabetic?
1. Evaluate Your Symptoms
If you think you might be prediabetic, evaluate and record your symptoms. Review the list of common symptoms above to get started. Once you know the symptoms of prediabetes, write down any that you experience and when you first noticed them. This could be as simple as writing them down on a piece of notebook paper or making a note on your phone.
When recording your symptoms, try to be as thorough and specific as possible. For example, if you notice increased thirst or urination, write down the date you first experienced these symptoms and how long they persisted. You should also make a note of any other symptoms you experienced at the same time. By being as specific as possible, you can help your healthcare provider rule out other conditions that could be triggering your symptoms.
2. Call a Healthcare Professional
Diagnosing prediabetes before it develops into type 2 diabetes can improve your chances of reversing it and help limit further complications. If you are experiencing any symptoms of prediabetes or suspect you have it, make an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your options.
During your appointment, tell your healthcare provider if you have a family history of type 2 diabetes and if any other risk factors apply to you. Depending on your medical history and symptoms, they may recommend further testing to verify your diagnosis.
3. Test for Prediabetes
Your healthcare provider may recommend testing for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes if you are experiencing one or more of the symptoms discussed above or have another condition that increases your risk.
A glycated hemoglobin (A1c) test is a common testing option for monitoring blood sugar levels over time. This test indicates your average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months and measures the percentage of the hemoglobin in your red blood cells that are attached to sugar from your bloodstream.
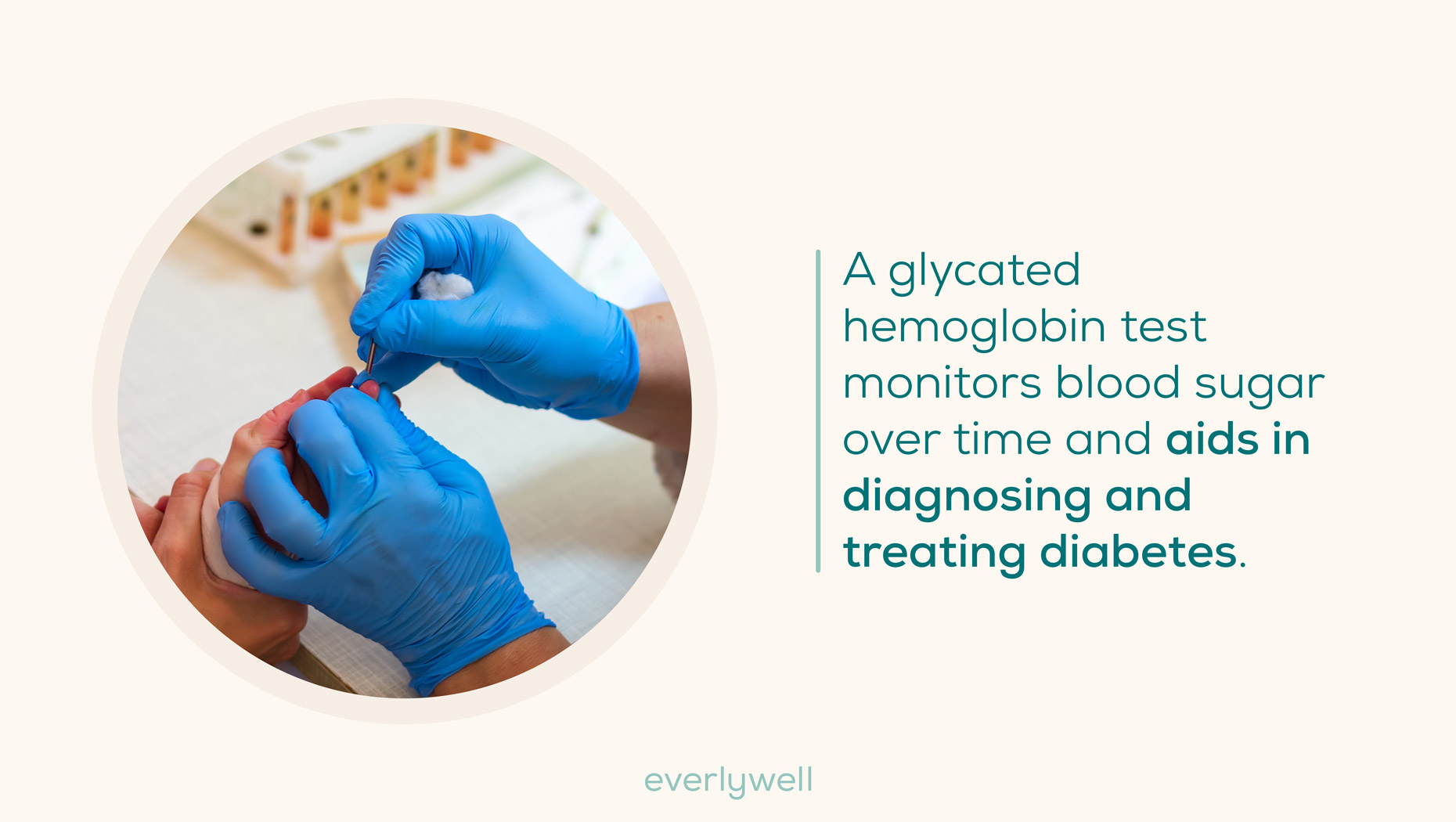
This is a test you can take at home with our at-home HbA1c Test. Taking the test is easy: you simply collect a small sample of blood via a simple finger prick and ship the sample to a lab for analysis (a prepaid shipping label is included with the kit).
In addition to an A1c test, you can also learn more about your glucose levels with a fasting blood sugar test or an oral glucose tolerance test. Your healthcare provider can let you know if they suggest any of these blood glucose level tests. If your results indicate you have prediabetes, your healthcare provider may recommend that you have your A1c levels retested every year.
Getting an early diagnosis is essential to help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later on. Remember to review the warning signs and discuss your symptoms and testing options with your healthcare provider if you suspect that you might have prediabetes.
Related Content
References
1. Prediabetes. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
2. Prediabetes - Diagnosis. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
3. Prediabetes - Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. URL.. Accessed May 15, 2020.
4. Prediabetes - Your Chance to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
5. A1C test. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
6. Glucose tolerance test. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
7. The Surprising Truth About Prediabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
8. A1C Between 5.7 and 6.4% as a Marker for Identifying Pre-Diabetes, Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. American Diabetes Association. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
9. Peripheral Neuropathy in Prediabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome. Journal of Diabetes Investigation. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
10. Diabetes Symptoms: When Diabetes Symptoms are a Concern. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
11. Insulin resistance. Cleveland Clinic. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
12. Ultraprocessed Food Consumption and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Among Participants of the NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort. JAMA Internal Medicine. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
13. Sleep Apnea in Type 2 Diabetes. American Diabetes Association. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
14. Diabetes Risk Factors. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
15. Cigarette Smoking: An Accessory to the Development of Insulin Resistance. National Center for Biotechnology Information. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
16. Fiber: The Carb that Helps You Manage Diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
17. Stress and Diabetes. Diabetes UK. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
18. Associations Between Poor Sleep and Glucose Intolerance in Prediabetes. National Center for Biotechnology Information. URL. Accessed July 14, 2022.
